A flower is the reproductive structure of angiosperm that facilitates sexual reproduction. The 4 main parts of the flower include – sepals, petals, stamens (male parts of the flower), and carpels (female part of the flower). The different parts of the flower have their unique function. The primary function of the flower is reproduction in plants, attracting pollinators for fertilization and producing seeds and fruits.
In this article we will study, parts of a flower and their function.
Table of Content
- What is a Flower?
- Parts of Flower Diagram
- Parts of Flower
- Whorls of Flowers
- Calyx
- Corolla
- Androecium
- Gynoecium
- Parts of Flower and Function
- Functions of Flower
- Conclusion – Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
- FAQs on Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
What is a Flower?
A flower is a reproductive structure found in flowering plants (angiosperms). It consists of two main parts: the male parts of the flower called stamens, which consist of a filament and an anther that produces pollen; and the female reproductive part known as the pistil or carpel, consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary where ovules are present. These reproductive parts of flower help in pollination and sexual reproduction.
Flowers can be classified into two main categories: complete and incomplete. A complete flower possesses all four whorls of parts—sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils. A complete flower consists of two different parts: Vegetative Part and Reproductive Part. On the other hand, an incomplete flower lacks one or more of these structures.
Parts of Flower Diagram
A well labelled diagram of the parts of the flower is as follows:
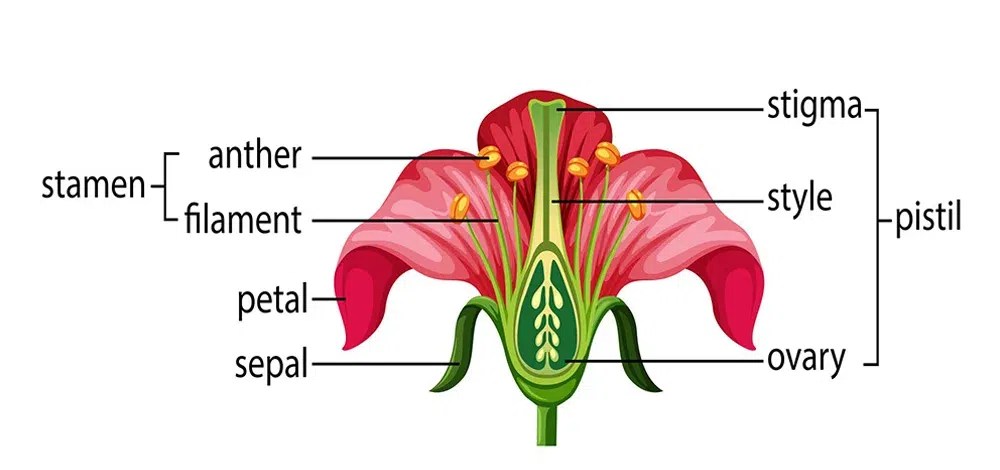
Diagram of Flower
Parts of Flower
The flower normally has four whorls, which are divided into essential whorl and accessory whorl. Essential whorl comprises gynoecium and androecium whereas Accessory whorl comprises Calyx and Corolla. The different parts of a flower are as follows:
Vegetative Part of a Flower
The vegetative part of a flower includes the sepals and petals, which are primarily involved in protecting the developing bud and attracting pollinators, respectively. These components are not directly related to the reproductive function of the flower but contribute to its overall structure and function. They are defined as follows:
- Sepal: Sepals are the outermost, usually green, leaf-like structures of a flower that protect the developing bud.
- Petal: Petals are the typically colorful, modified leaves of a flower that surround the reproductive parts of a flower and help to attract pollinators.
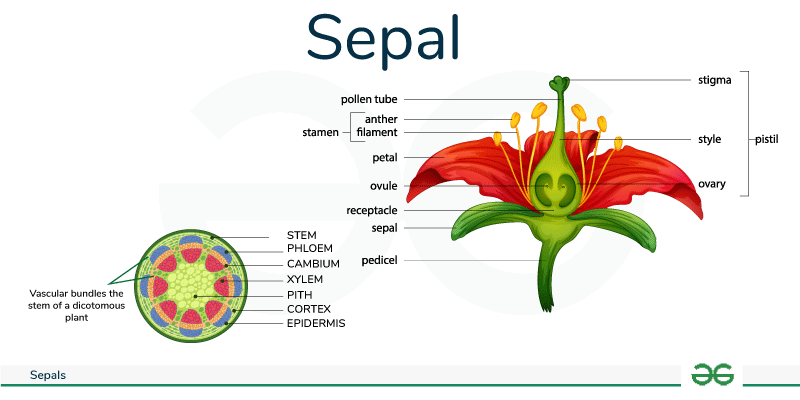
Sepal of Flowers
Reproductive Part of a Flower
The reproductive part of a flower consists of the stamens and the pistil (or carpel). Stamens are the male reproductive organs, producing pollen containing male gametes. The pistil is the female reproductive organ, containing the stigma, style, and ovary, where the female gametes (ovules) are located. These parts play a central role in pollination and fertilization, ensuring the plant’s reproduction.
Let’s discuss each part in detail.
Whorls of Flowers
In a flower, there are mainly four whorls of floral parts. The outermost whorl is the calyx, composed of sepals; the next is the corolla, made up of petals; followed by the androecium, which contains the stamens; and finally, the innermost whorl is the gynoecium, containing the pistil or carpel. These whorls collectively define the reproductive parts of flowers and structure. These four whorls are as follows:
Calyx
The outermost green protective whorl of the plant is known as calyx. Unit of the calyx is sepal. The initial layer in the flower structure is calyx. They are said to be modified leaves. Hence, the collection of sepals is called the calyx. The sepal or calyx is green in colour and its chief function is to protect the flower.
The calyx may be gamosepalous ( sepals united) or polysepalous (sepals free). It encloses the unopened bud. They perform a protective role for the flower earlier than it opens and afterwards put forth from the base of the flower.
Modifications of Calyx
- Spiny Calyx: When calyx gets modified in the form of spines. These are spiny calyx. Example- Trapa bispinosa (water chestnut) the calyx is spinous in the fruit.
- Persistent Calyx: When calyx remains attached to the fruit is called the persistent calyx. Example – Brinjal and tomato. Solanaceae family shows persistent calyx.
- Leafy Calyx: Sometimes calyx converts into a leaf-like structure and is called the leafy calyx. Example- Mussaenda.
Corolla
Corolla is the second accessory whorl a flower made up of petals. The collection of petals is known as Corolla. It is just beneath the calyx. Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination calyx and corolla together forms the perianth,the non-reproductive portion of the flower. The corolla may be gamopetalous (petals united) or polypetalous (petals free). The corolla part of flower varies greatly in plants with shape and colour. It may be tubular-shaped, funnel-shaped or wheel-shaped.
Types of Corolla
- Cruciform: When four petals in a flower are separated. It is a type of polypetalous corolla and is the characteristic of the family Brassicaceae. It is a regular corolla. Hence, the cruciform corolla is found in radish and mustard.
- Rosaceous: When 5 petals of a flower are spread. Hence, rosaceous corolla is found in roses which have corolla of 5 broad petals.
- Bell Shaped: Bell-shaped corolla is called campanulate. In this type, the corolla is present in the bell-shaped structure. example – campanula, and physalis.
Functions of Corolla
- Pollination: Since corolla is the attractive part of a flower and the petals are brightly coloured .moreover, it releases an aromatic smell which catches the insect’s attention like birds, bees, etc those help in the pollination of the flower and is known as pollinating agents.
- Protection of essential Whorl: Corolla protects the essential whorl i.e androecium and gynoecium ,the reproductive parts of a flower that participate in the fertilisation of the flower to produce fruit.
- Storage Part: Petals function as the storage house of sugar-rich nectar, attracting pollinating agents .
- Reproduction: Corolla directly does not take part in pollination but helps to attraction pollinating agents and perform pollination .its main function is to assist in the reproductive process of a plant.reproduction in plants occurs by the method of pollination.
Also Read: Types of Pollination
Androecium
The androecium is an essential whorl of the plant and it is considered as Male Reproductive Organ of the plant. It consists of stamen each of which consists of an anther and filament which produces pollen grain. Collectively the stamens form the androecium. Pollen grains are produced in pollen- sacs. A sterile stamen is called Staminode. It is a sterile flower which cannot participate in reproduction. For example Caesalpinioideae family.
When stamens are attached to the petals,the condition is called Epipetalous. Example-Brinjal. or Epiphyllous, when stamens are attached to the perianth. Example: Lily.
Function of Androecium
- Production of Pollen Grains: Its main function is to produce microspores i.e, pollen grains containing male gametes within anther lobe. Androecium serves the purpose of fertilisation in flowering plants.
- Pollination: Androecium consists of stamens which have 2 parts: anther and filament. anther helps to protect, store and produce pollen grain and the filament holds the anther up. these parts help the pollinating agents to perform pollination.
Gynoecium
The gynoecium is the second essential whorl of the plant or the innermost whorl and is considered a Female reproductive organ of the plant. It is surrounded by the androecium. the structural unit of gynoecium is Carpel. It consists of three parts Stigma, Style and Ovary. when more than one carpel is present, they may be free and are called Apocarpous. Example: Rose and lotus. They are termed Syncarpous when carpels are fused. Example: Mustard and tomato.
Parts of Gynoecium
- Stigma: Stigma is a receptive surface of gynoecium for receiving pollen grain. it is at the tip of the style.
- Style: Style is a tube-like structure in which the way of pollen grains move towards the ovary.
- Ovary: Lower swollen part of gynoecium is known as ovary. The ovary consists of the ovule and within the ovule, embryo sac is present where double fertilisation takes place.
Function of Gynoecium
- Fertilization: Fertilisation takes place in the gynoecium. the gynoecium develops into seeds and fruits after fertilisation.
- Protection: Gynoecium plays an important role in producing and protecting ovules.
Parts of Flower and Function
The table below shows the flower parts and their functions:
Flower Parts | Function |
Receptacles | provides support for the floral organs and serves as the attachment point for the other floral parts. |
Sepals | protect the developing flower bud during budding stage |
Petals | attract pollinators like bees, butterflies to aid in pollination |
Stamens | male reproductive part of flower |
Carpel | female reproductive part of flower |
Functions of Flower
The function of the flower are as follows:
- The primary function of a flower is to facilitate the reproduction of the plant by producing seeds through pollination and fertilization.
- Flowers use their colors, fragrances, and nectar to attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, birds, and insects, which aid in the transfer of pollen between flowers.
- Sepals, the outermost part of a flower, protect the developing bud from damage, harsh weather, and herbivores
- Flowers facilitate the process of fertilization by bringing together pollen from the stamens to the stigma of the pistil, allowing for the fusion of male and female gametes.
- After successful fertilization, flowers develop seeds within the ovary, which can later be dispersed for the growth of new plants.
- Flowers contribute to biodiversity by supporting a wide range of pollinators and providing essential resources for various species within ecosystems.
- Some flowers, such as those of fruit-bearing plants, develop into fruits that protect and nourish the seeds, making them more appealing to animals for dispersal.
Also Read: Sexual reproduction in plants
Conclusion – Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
In summary, the parts of flower consists of – sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil. Understanding the various parts of a flower provides insight into its essential role in plant reproduction. The colourful petals attract pollinators to help in the process of pollination and sepals provides protection to the developing buds in budding stage. The male reproductive part of flower is called stamen and the female reproductive part is known as carpel.
Also Read:
- Inflorescence
- Aestivation in Plant: Definition, Types, Examples
- Morphology of Flower – Definition, Structure, Parts, Examples
- The Role of Sepals in Flower Development and Protection
FAQs on Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
What are the Parts of the Flower Class 4th?
The parts of flowers include – Petals, sepals, stamen, pistil.
What is a Flower in Science?
A flower is a reproductive structure of angiosperms.
What is the Function of the Flower Class 6?
Function of the flower includes reproduction through pollination and seed formation.
What are the Parts of the Flower and its Functions?
Parts of the flower and their functions: Petals attract pollinators, sepals protect the flower, stamen produces pollen, pistil contains ovules.
What are the 4 Functions of a Flower?
Four functions of a flower: Reproduction, attracting pollinators, protecting reproductive structures, seed formation.
What is the Function of Each Part of the Plant?
Function of each part of the plant includes – Petals attract pollinators for reproduction.
What is the Function of Petals?
Function of petals is attracting pollinators to help in reproduction.
khushbubhandari9
Improve
Previous Article
Morphology of Flower - Definition, Structure, Parts, Examples
Next Article
Androecium - Definition, Components, Structure, Functions
